Recursive Traversal
递归的方法的空间复杂度为O(n)。
节点的定义如下:
// Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
}
Preorder Traversal
void preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& nums) {
if(!root) return;
nums.push_back(root->val);
preorderTraversal(root->left);
preorderTraversal(root->right);
}
Inorder Traversal
void inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& nums) {
if(!root) return;
inorderTraversal(root->left, nums);
nums.push_back(root->val);
inorderTraversal(root->right, nums);
}
Postorder Traversal
void postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& nums) {
if(!root) return;
postorderTraversal(root->left, nums);
postorderTraversal(root->right, nums);
nums.push_back(root->val);
}
Iterative Traversal
迭代方法需要使用stack来保存遍历路径上待遍历的节点,从根节点到叶节点,最多保存n/2个节点。空间复杂度为O(n)。
Preorder Traversal
// Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
// 使用栈,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<const TreeNode *> s;
if (root != nullptr) s.push(root);
while (!s.empty()) {
const TreeNode *p = s.top();
s.pop();
result.push_back(p->val);
if (p->right != nullptr) s.push(p->right);
if (p->left != nullptr) s.push(p->left);
}
return result;
}
};
void preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> nums;
vector<int> nums;
stack<TreeNode* > st; // pointers in stack are valid
while (root || !st.empty()) {
if (!root) {
root = st.top();
st.pop();
}
nums.push_back(root->val);
// if valid right child, push into stack
if (root->right) st.push(root->right);
// go to the left child
root = root->left;
}
return nums;
}
Inorder Traversal
// Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
// 使用栈,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<const TreeNode *> s;
const TreeNode *p = root;
while (!s.empty() || p != nullptr) {
if (p != nullptr) {
s.push(p);
p = p->left;
} else {
p = s.top();
s.pop();
result.push_back(p->val);
p = p->right;
}
}
return result;
}
};
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> nums;
stack<TreeNode* > st; // pointers in stack are valid
while (root || !st.empty()) {
if (root) {
// push root into stack, then go left
st.push(root);
root = root->left;
} else {
// for nodes in stack, only visit its right
root = st.top();
st.pop();
nums.push_back(root->val);
root = root->right;
}
}
return nums;
}
Postorder
// Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
// 使用栈,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector<int> result;
stack<const TreeNode *> s;
/* p,正在访问的结点,q,刚刚访问过的结点*/
const TreeNode *p = root, *q = nullptr;
do {
while (p != nullptr) { /* 往左下走*/
s.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
q = nullptr;
while (!s.empty()) {
p = s.top();
s.pop();
/* 右孩子不存在或已被访问,访问之*/
if (p->right == q) {
result.push_back(p->val);
q = p; /* 保存刚访问过的结点*/
} else {
/* 当前结点不能访问,需第二次进栈*/
s.push(p);
/* 先处理右子树*/
p = p->right;
break;
}
}
} while (!s.empty());
return result;
}
};
后序遍历可以看作是和前序遍历是左右对称的,从根节点开始,先遍历右子树,再遍历左子树,只不过为了得到后序遍历的输出,我们需要遍历结果逆序输出。可以比较前序遍历的代码,逻辑完全是一样的,就是左右子树访问顺序交换了,完全是对称的。
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> nums;
stack<TreeNode* > stnode;
while (root || !stnode.empty()) {
if (!root) {
root = stnode.top();
stnode.pop();
}
nums.push_back(root->val);
if (root->left) stnode.push(root->left);
root = root->right;
}
return vector<int>(nums.rbegin(), nums.rend())
}
- Iterative Postorder Traversal | Set 1 (Using Two Stacks)
- Iterative Postorder Traversal | Set 2 (Using One Stack)
Morris Traversal
Morris遍历方法不需要栈来保存待访问的节点,而是通过利用节点本身的指针来保存待访问节点的指针,并在访问过程中恢复节点。实现了O(1)空间复杂度。
Preorder Traversal
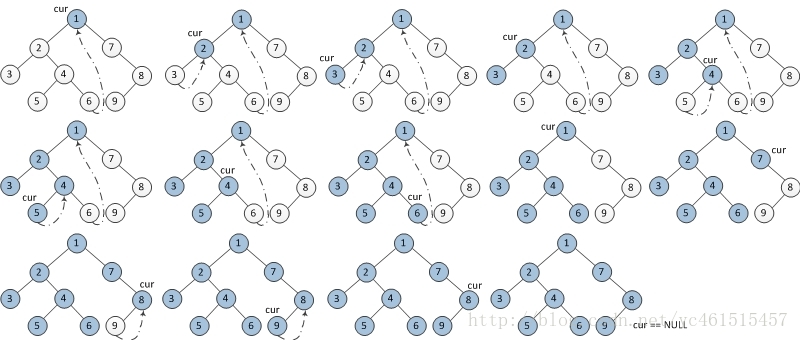
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
// morris traversal
vector<int> nums;
TreeNode* cur = nullptr;
while (root) {
if (root->left) {
cur = root->left;
// find the predecessor of root node
while (cur->right && cur->right != root) { cur = cur->right;
}
// has visited this root node
if (cur->right == root) {
cur->right = nullptr;
root = root->right;
} else {
nums.push_back(root->val);
cur->right = root;
root = root->left;
}
} else {
nums.push_back(root->val);
root = root->right;
}
}
return nums;
}
// Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
// Morris先序遍历,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector preorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector result;
TreeNode *cur = root, *prev = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr) {
if (cur->left == nullptr) {
result.push_back(cur->val);
prev = cur; /* cur刚刚被访问过 */
cur = cur->right;
} else {
/* 查找前驱 */
TreeNode *node = cur->left;
while (node->right != nullptr && node->right != cur)
node = node->right;
if (node->right == nullptr) { /* 还没线索化,则建立线索 */
result.push_back(cur->val); /* 仅这一行的位置与中序不同 */
node->right = cur;
prev = cur; /* cur刚刚被访问过 */
cur = cur->left;
} else { /* 已经线索化,则删除线索 */
node->right = nullptr;
/* prev = cur; 不能有这句,cur已经被访问 */
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
Inorder Traversal
中序和前序代码基本一样,唯一不同的在输出节点值的顺序不同。
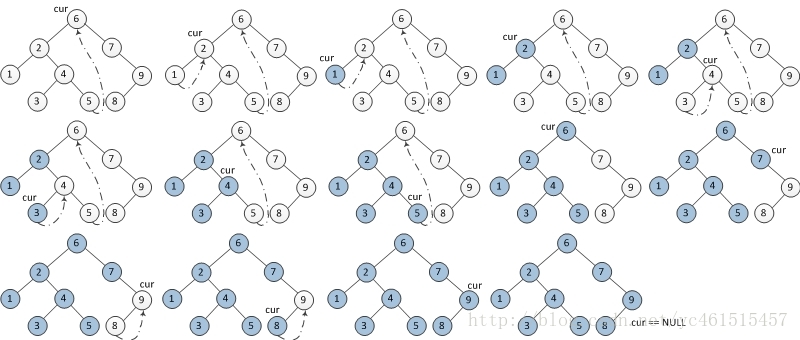
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> nums;
TreeNode* cur = nullptr;
while (root) {
if (root->left) {
cur = root->left;
while (cur->right && cur->right != root) {
cur = cur->right;
}
if (cur->right == root) {
nums.push_back(root->val);
cur->right = nullptr;
root = root->right;
} else {
cur->right = root;
root = root->left;
}
} else {
nums.push_back(root->val);
root = root->right;
}
}
return nums;
}
}
// Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
// Morris中序遍历,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector inorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector result;
TreeNode *cur = root, *prev = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr) {
if (cur->left == nullptr) {
result.push_back(cur->val);
prev = cur;
cur = cur->right;
} else {
/* 查找前驱 */
TreeNode *node = cur->left;
while (node->right != nullptr && node->right != cur)
node = node->right;
if (node->right == nullptr) { /* 还没线索化,则建立线索 */
node->right = cur;
/* prev = cur; 不能有这句,cur还没有被访问 */
cur = cur->left;
} else { /* 已经线索化,则访问节点,并删除线索 */
result.push_back(cur->val);
node->right = nullptr;
prev = cur;
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
Postorder Traversal
之前我们在讲迭代方法时,说过了后序遍历其实可以看作是和前序遍历左右对称的,此处,我们同样可以利用这个性质,基于前序遍历的算法,可以很快得到后序遍历的结果。我们只需要将前序遍历中所有的左孩子和右孩子进行交换就可以了。
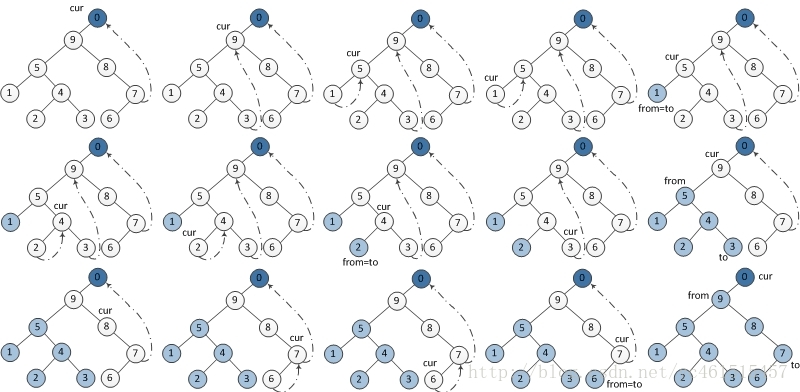
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> nums;
TreeNode* cur = nullptr;
while (root) {
if (root->right) {
cur = root->right;
while (cur->left && cur->left != root) {
cur = cur->left;
}
if (cur->left == root) {
cur->left = nullptr;
root = root->left;
} else {
nums.push_back(root->val);
cur->left = root;
root = root->right;
}
} else {
nums.push_back(root->val);
root = root->left;
}
}
return vector<int>(nums.rbegin(), nums.rend());
}
// Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
// Morris后序遍历,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector postorderTraversal(TreeNode *root) {
vector result;
TreeNode dummy(-1);
TreeNode *cur, *prev = nullptr;
std::function < void(const TreeNode*)> visit =
[&result](const TreeNode *node){
result.push_back(node->val);
};
dummy.left = root;
cur = &dummy;
while (cur != nullptr) {
if (cur->left == nullptr) {
prev = cur; /* 必须要有 */
cur = cur->right;
} else {
TreeNode *node = cur->left;
while (node->right != nullptr && node->right != cur)
node = node->right;
if (node->right == nullptr) { /* 还没线索化,则建立线索 */
node->right = cur;
prev = cur; /* 必须要有 */
cur = cur->left;
} else { /* 已经线索化,则访问节点,并删除线索 */
visit_reverse(cur->left, prev, visit);
prev->right = nullptr;
prev = cur; /* 必须要有 */
cur = cur->right;
}
}
}
return result;
}
private:
// 逆转路径
static void reverse(TreeNode *from, TreeNode *to) {
TreeNode *x = from, *y = from->right, *z;
if (from == to) return;
while (x != to) {
z = y->right;
y->right = x;
x = y;
y = z;
}
}
// 访问逆转后的路径上的所有结点
static void visit_reverse(TreeNode* from, TreeNode *to,
std::function< void(const TreeNode*) >& visit) {
TreeNode *p = to;
reverse(from, to);
while (true) {
visit(p);
if (p == from)
break;
p = p->right;
}
reverse(to, from);
}
};